前言
NOIp2017已经结束了,由于复赛结束后我没有机会写游记,到这个周末才补上。虽然下个星期期中考
初赛日期2017/10/14,复赛2017/11/11和12,今年还是衢州。本文只包含复赛。
值得一提的是,复赛day1双十一和马拉松,day(-1)和day0是学校秋季运动会,当然我们甚至没机会去看开幕式。
day0
上午有一场两个半小时的模拟赛,题目确实不难,但是我只有230,而很多人都300,没什么信心。
T3给定一棵树,求保留最少的边使得覆盖的点不少于K,由于一条边可以覆盖1或2个点,可以用树形DP或贪心求出最多有几条边可以覆盖2个点,而我却写了二分图匹配,还写错了。还好交了暴力的30分。
12:30我们准时从西门出发,预计三个小时到,最终到四点左右才到达衢州饭店。路上基本也没干什么。
衢州饭店还是比较好的,我们住在三号楼一楼,要走过很长的走廊。矿泉水一个人一小瓶,杯子倒是很多。拖鞋是循环使用的,所以不能带走。我选了靠窗的床,事实证明还是很对的,因为可以方便放东西。无线网不太稳定,反而还是旁边的比较好。
从旅馆到衢州二中堵了很长时间,到学校领袋子,晚饭在学校吃。回去就快多了。晚上看了洛谷模板,包括(下次可以参考)
- SSSP
- KMP(看完认为还是滚回hash吧)
- Dinic(初赛暗示网络流?)
- 可并堆(还是不太会)
- LCA(上午刚写过)
- 树剖
- 匈牙利
- Tarjan割边割点
- Lucas
- exgcd(初赛前也看过)
我看了一会儿WARRIORS:Omen of The Stars #6 The Last Hope,再来一句StarClan, light my path, please. 规划好day1要带的物品后,我们十点多睡觉。
day1
6:20起床,去吃自助餐,并不是很好。我在9号考场,要走不少路才能到,不过去年也一样。
OS是Windows 7,我打开了仪表盘。果然没有Notepad++。
小凯的疑惑(math)
题意
给定$a,b\vert (a,b)=1$,求$ax+by\vert x,y\in\mathbb N$不能表示的最大的数,保证有解。
1
3 7
1
11
数据范围
- 对于30%的数据,$a,b\le50$
- 对于60%的数据,$a,b\le10,000$
- 对于100%的数据,$1\le a,b\le10^9$
思路
看到这题我立刻想到了一道USACO的题目,猜想答案应该不大于$ab+a+b$。对于$ax+by=1$,用exgcd求出$x_0,y_0$,然后枚举$c$,解为$cx_0+kb,cy_0-kb$,强制$x\ge0$,如果$y<0$显然无解。不过我不知道复杂度,后来还列出了一个带上取整的不等式,解出的结果只含有$a,b$,但是样例都不对,于是我放弃了。直接从$ab$向下枚举,输出第一个无解的数。好像$a,b\le10^6$都能很快算出。
时间复杂度$\mathcal O(?)$,预计得分60/60+
结束后才知道大部分人都做出了这题,答案是$ab-a-b$。所以我的时间复杂度为$\mathcal O(a+b)$。
代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
#include <fstream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
ifstream fin("math.in");
ofstream fout("math.out");
void exgcd(int a, int b, long long &x, long long &y)
{
if (!b)
{
x = 1;
y = 0;
}
else
{
exgcd(b, a % b, y, x);
y -= a / b * x;
}
}
int main()
{
int a, b;
fin >> a >> b;
if (a > b)
swap(a, b);
long long x, y;
exgcd(a, b, x, y);
for (long long c = 1ll * a * b; c >= 0; c--)
{
long long k = -x * c / b;
if (x * c + 1ll * k * b < 0)
k++;
long long ny = y * c - 1ll * k * a;
if (ny < 0)
{
fout << c << endl;
return 0;
}
}
return 0;
}
用来对拍的暴力:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
ifstream fin("math.in");
ofstream fout("math.ans");
int main()
{
int a, b;
fin >> a >> b;
for (int c = a * b + a + b; c; c--)
{
bool flag = false;
for (int i = 0; i <= c; i += a)
if ((c - i) % b == 0)
{
flag = true;
break;
}
if (!flag)
{
fout << c << endl;
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
时间复杂度(complexity)
题意
给定一个$L$行只含有for循环的程序,初值和末值可以是常数或$n$,判断其复杂度分析是否正确。可能存在循环不匹配和变量重名错误需要判断。多组数据。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
8
2 O(1)
F i 1 1
E
2 O(n^1)
F x 1 n
E
1 O(1)
F x 1 n
4 O(n^2)
F x 5 n
F y 10 n
E
E
4 O(n^2)
F x 9 n
E
F y 2 n
E
4 O(n^1)
F x 9 n
F y n 4
E
E
4 O(1)
F y n 4
F x 9 n
E
E
4 O(n^2)
F x 1 n
F x 1 10
E
E
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Yes
Yes
ERR
Yes
No
Yes
Yes
ERR
数据范围
- 对于30%的数据,数据保证小明给出的每个程序的前$L/2$行一定为以
F开头的语句,第$L/2+1$行至第$L$行一定为以E开头的语句,$L\le10$。 - 对于50%的数据,若$x,y$均为整数,$x$一定小于$y$,且只有$y$有可能为$n$。
- 对于70%的数据,不存在语法错误。
- 对于100%的数据,$L\le100$。
思路
麻烦的题目,不过我自认为有优势,看起来有点像COWBASIC。$n$和常数怎么判断呢?不过我很快想到了数值法,把很大的数代入$n$,求一下实际复杂度和理论复杂度,如果误差是很小的则认为正确。
接下来的问题在于确定$n$的值。一开始我以为最多有50层循环,后来发现由于字母的限制最多只有25层。一开始我选择了,后来发现太小了。最终我选择了,用double计算。最大误差取$0.01$。
还有表达式计算的问题,我发现每层栈里应该保存该层循环次数和该层累计的数值。
时间复杂度$\mathcal O(L)$,预计得分100
结束后才得知只需要模拟一下,因为每层循环只能执行$0$,$\Theta(1)$或$\Theta(n)$次。注意判断执行$0$次时的问题即可。
代码
很长……调了不少时间
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
#include <sstream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
ifstream fin("complexity.in");
ofstream fout("complexity.out");
const int N = 105, vn[] = {1000000000, 2000000000};
double s[N][2], res[2];
bool vis[26];
struct line
{
int opt, l, r;
} prog[N];
int str2int(const string &s)
{
stringstream ss(s);
int x;
ss >> x;
return x;
}
double calc(const line &p, int n)
{
int l = p.l, r = p.r;
if (l == 1000)
l = n;
if (r == 1000)
r = n;
return max(r - l + 1, 0);
}
int main()
{
int t;
fin >> t;
while (t--)
{
int l;
string comp;
fin >> l >> comp;
memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis));
bool valid = true;
string st;
for (int i = 1; i <= l; i++)
{
char opt;
fin >> opt;
if (opt == 'F')
{
char var;
string l, r;
fin >> var >> l >> r;
if (vis[var - 'a'])
valid = false;
vis[var - 'a'] = true;
st += var;
prog[i].opt = 1;
if (l == "n")
prog[i].l = 1000;
else
prog[i].l = str2int(l);
if (r == "n")
prog[i].r = 1000;
else
prog[i].r = str2int(r);
}
else
{
if (st == "")
valid = false;
else
{
vis[st[st.length() - 1] - 'a'] = false;
st.erase(st.length() - 1, 1);
}
prog[i].opt = 2;
}
}
if (st != "")
valid = false;
if (!valid)
{
fout << "ERR\n";
continue;
}
for (int t = 0; t < 2; t++)
{
s[0][1] = .0;
int sp = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= l; i++)
if (prog[i].opt == 1)
{
s[++sp][0] = calc(prog[i], vn[t]);
s[sp][1] = .0;
}
else
{
if (s[sp][1] == .0)
s[sp][1] = 1.;
s[sp - 1][1] += s[sp][0] * s[sp][1];
sp--;
}
double th;
if (comp == "O(1)")
th = 1.;
else
th = pow(vn[t], str2int(comp.substr(4, comp.length() - 5)));
if (s[0][1] == .0)
s[0][1] = 1.;
res[t] = s[0][1] / th;
}
if (fabs(1 - res[0] / res[1]) < 0.01)
fout << "Yes\n";
else
fout << "No\n";
}
return 0;
}
逛公园(park)
题意
求有向图中$1->N$长度不超过$d+K$的路径数,其中$d$为$1->N$的最短路长度,可能有0边,如果有无穷条合法路径输出$-1$。多组数据
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
2
5 7 2 10
1 2 1
2 4 0
4 5 2
2 3 2
3 4 1
3 5 2
1 5 3
2 2 0 10
1 2 0
2 1 0
1
2
3
-1
数据范围
| 测试点编号 | $T$ | $N$ | $M$ | $K$ | 是否有0边 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5 | 5 | 10 | 0 | 否 |
| 2 | 5 | 1000 | 2000 | 0 | 否 |
| 3 | 5 | 1000 | 2000 | 50 | 否 |
| 4 | 5 | 1000 | 2000 | 50 | 否 |
| 5 | 5 | 1000 | 2000 | 50 | 否 |
| 6 | 5 | 1000 | 2000 | 50 | 是 |
| 7 | 5 | 100000 | 200000 | 0 | 否 |
| 8 | 3 | 100000 | 200000 | 50 | 否 |
| 9 | 3 | 100000 | 200000 | 50 | 是 |
| 10 | 3 | 100000 | 200000 | 50 | 是 |
思路
T2用了较多时间。毫无思路,当然$K=0$就是最短路计数,而$K>0$好像可以用K短路之类的方法。于是我还求了$N$为起点的最短路,然后从$1$开始dfs,如果当前距离+最短路$>d+K$剪枝。不知道有多少分。
时间复杂度,预计得分30/30+
代码
这份代码没有包含functional,在VC++下std::greater<state>未定义。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
#include <fstream>
#include <queue>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
ifstream fin("park.in");
ofstream fout("park.out");
const int N = 100005, M = 200005, INF = 1e9;
int n, m, k, p, head[N], v[M], w[M], nxt[M], e, d[N], f[N];
int rhead[N], rv[M], rw[M], rnxt[M], re, rd[N], ans;
bool vis[N];
inline void add_edge(int u, int v, int w)
{
::v[++e] = v;
::w[e] = w;
nxt[e] = head[u];
head[u] = e;
}
inline void radd_edge(int u, int v, int w)
{
::rv[++re] = v;
::rw[re] = w;
rnxt[re] = rhead[u];
rhead[u] = re;
}
void dfs(int u, int dist)
{
if (dist + rd[u] > d[n] + k)
return;
if (u == n)
{
ans = (ans + 1) % p;
return;
}
for (int i = head[u]; i; i = nxt[i])
dfs(v[i], dist + w[i]);
}
int main()
{
int t;
fin >> t;
while (t--)
{
fin >> n >> m >> k >> p;
e = re = 0;
fill(head + 1, head + n + 1, 0);
fill(rhead + 1, rhead + n + 1, 0);
while (m--)
{
int u, v, w;
fin >> u >> v >> w;
add_edge(u, v, w);
radd_edge(v, u, w);
}
typedef pair<int, int> state;
fill(d + 1, d + n + 1, INF);
d[1] = 0;
priority_queue<state, vector<state>, greater<state>> Q;
Q.push(make_pair(0, 1));
fill(f + 1, f + n + 1, 0);
f[1] = 1;
fill(vis + 1, vis + n + 1, false);
while (!Q.empty())
{
state k = Q.top();
Q.pop();
if (vis[k.second])
continue;
vis[k.second] = true;
for (int i = head[k.second]; i; i = nxt[i])
if (d[k.second] + w[i] < d[v[i]])
{
f[v[i]] = f[k.second];
Q.push(make_pair(d[v[i]] = d[k.second] + w[i], v[i]));
}
else if (d[k.second] + w[i] == d[v[i]])
(f[v[i]] += f[k.second]) %= p;
}
if (k == 0)
fout << f[n] << endl;
else
{
fill(rd + 1, rd + n + 1, INF);
rd[n] = 0;
priority_queue<state, vector<state>, greater<state>> Q;
Q.push(make_pair(0, n));
fill(vis + 1, vis + n + 1, false);
while (!Q.empty())
{
state k = Q.top();
Q.pop();
if (vis[k.second])
continue;
vis[k.second] = true;
for (int i = rhead[k.second]; i; i = rnxt[i])
if (rd[k.second] + rw[i] < rd[rv[i]])
Q.push(make_pair(rd[rv[i]] = rd[k.second] + rw[i], rv[i]));
}
ans = 0;
dfs(1, 0);
fout << ans << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
剩下的时间
听说很多人都会做T1和T3,大多200+,我感到很绝望,希望T2不要炸。听说T1是小学奥数题,以及有人做过原题。而T3则是“图论算法集合”?
下午没看几页书,晚饭据说从学校打包到旅馆,还必须在员工餐厅里吃,不过zyy好像早跑了。晚上看了一集下午的《自然传奇》,心态好了很多。fks提出敲一下[ZJOI2008]树的统计,他很快就A了,我很害怕没去写,万一真的考了树剖呢。不过吸取一下把int开成char的教训。睡得比前一天早。
day2
奶酪(cheese)
题意
一块长宽无限高为$h$的奶酪里有$n$个半径均为$r$的空洞,下表面$z=0$,上表面$z=h$。两个空洞相交或相切可以从一个到达另一个,与表面相交或相切则可以从表面到达空洞。求能否从下表面到达上表面。多组数据
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
3
2 4 1
0 0 1
0 0 3
2 5 1
0 0 1
0 0 4
2 5 2
0 0 2
2 0 4
1
2
3
Yes
No
Yes
数据范围
- 对于20%的数据,$n=1$
- 对于40%的数据,$n\le8$
- 对于80%的数据,$h,r,\vert x\vert,\vert y\vert,\vert z\vert\le10,000$
- 对于100%的数据,$1\le n\le1,000,1\le h,r,\vert x\vert,\vert y\vert,\vert z\vert\le10^9$
思路
计算几何,吃笔记本稳了?分治?不过看到$n\le1,000,T\le20$就很简单了,不就是直接bfs。注意一下long long应该就可以了吧。不会卡常吧?
时间复杂度$\mathcal O(Tn^2)$,预计得分100
果然那么简单还是有陷阱的,$(2\times10^9)^2\times3=12\times10^{18}>2^{63}$!所以要unsigned long long或者把左边的一项移到不等式右边。只有80了。
让我欣慰的是,有人直接用浮点数开根,可能被卡常,还有人用了int……另外据说$z\ge0$。
代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
#include <fstream>
#include <queue>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
ifstream fin("cheese.in");
ofstream fout("cheese.out");
const int N = 1005;
int x[N], y[N], z[N];
bool vis[N];
inline long long sqr(long long x)
{
return x * x;
}
int main()
{
int t;
fin >> t;
while (t--)
{
int n, h, r;
fin >> n >> h >> r;
queue<int> Q;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
fin >> x[i] >> y[i] >> z[i];
if (abs(z[i]) <= r)
{
vis[i] = true;
Q.push(i);
}
else
vis[i] = false;
}
while (!Q.empty())
{
int k = Q.front();
Q.pop();
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
if (!vis[j] && sqr(x[k] - x[j]) + sqr(y[k] - y[j]) + sqr(z[k] - z[j]) <= 4 * sqr(r))
{
vis[j] = true;
Q.push(j);
}
}
bool ans = false;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
if (vis[i] && abs(z[i] - h) <= r)
{
ans = true;
break;
}
if (ans)
fout << "Yes\n";
else
fout << "No\n";
}
return 0;
}
宝藏(treasure)
题意
给定一张无向图,需要选定一个点$s$,每条边的代价$c_i=w_i\times(\min(dist_{s,u_i},dist_{s,v_i})+1)$,求生成树最小代价和。
1
2
3
4
5
6
4 5
1 2 1
1 3 3
1 4 1
2 3 4
3 4 1
1
4
数据范围
- 对于20%的数据,保证输入是一棵树
- 对于40%的数据,所有$w_i$相等
- 对于70%的数据,$n\le8,w_i\le5,000$
- 对于100%的数据,$1\le n\le12,0\le m\le1,000,w_i\le500,000$
思路
重边显然取min,这样边数只有$\frac{n(n-1)}2$,但好像基于边比较难做。似乎暴力也很难写,但我yy出了一种奇怪的做法:类似Prim,每次选择一个不在生成树中的点加入,更新最短路,然后继续搜。具体见代码。如果无解怎么办?
时间复杂度$\mathcal O(n^3n!)$,预计得分70
应该是状压DP,还有人写了多项式复杂度的贪心。
代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
#include <fstream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
ifstream fin("treasure.in");
ofstream fout("treasure.out");
const int N = 15, INF = 1e9;
int n, m, mat[N][N], d[N], ans;
void dfs(int k, int now)
{
if (now > ans)
return;
if (k == n)
ans = now;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
if (d[i] < INF)
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
if (mat[i][j] && d[j] == INF)
{
d[j] = d[i] + 1;
dfs(k + 1, now + mat[i][j] * (d[i] + 1));
d[j] = INF;
}
}
int main()
{
fin >> n >> m;
while (m--)
{
int u, v, w;
fin >> u >> v >> w;
if (!mat[u][v] || w < mat[u][v])
mat[u][v] = mat[v][u] = w;
}
ans = INF;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
fill(d + 1, d + n + 1, INF);
d[i] = 0;
dfs(1, 0);
}
fout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
列队(phalanx)
题意
给定一个$n\times m$的矩阵$A$,$A_{i,j}=(i-1)m+j$。$q$次操作($n,m,q\le3*10^5$),每次删除一个位置$(x,y)$,然后将第$x$行向左补齐,再将第$m$列向前补齐,最后在$A_{n,m}$填上删除的数。求每次删除的数。
1
2
3
4
2 2 3
1 1
2 2
1 2
1
2
3
1
1
4
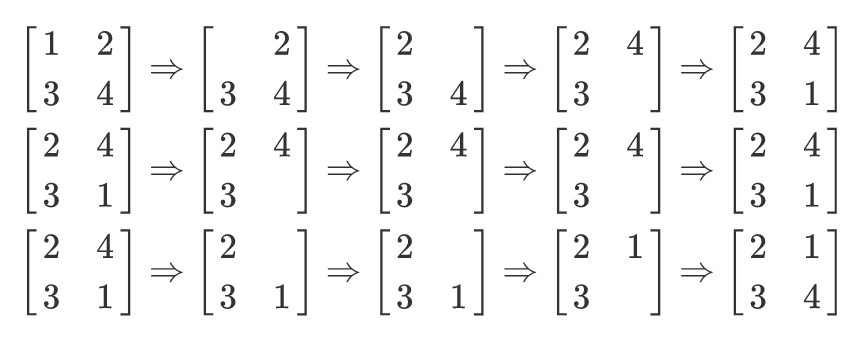
数据范围
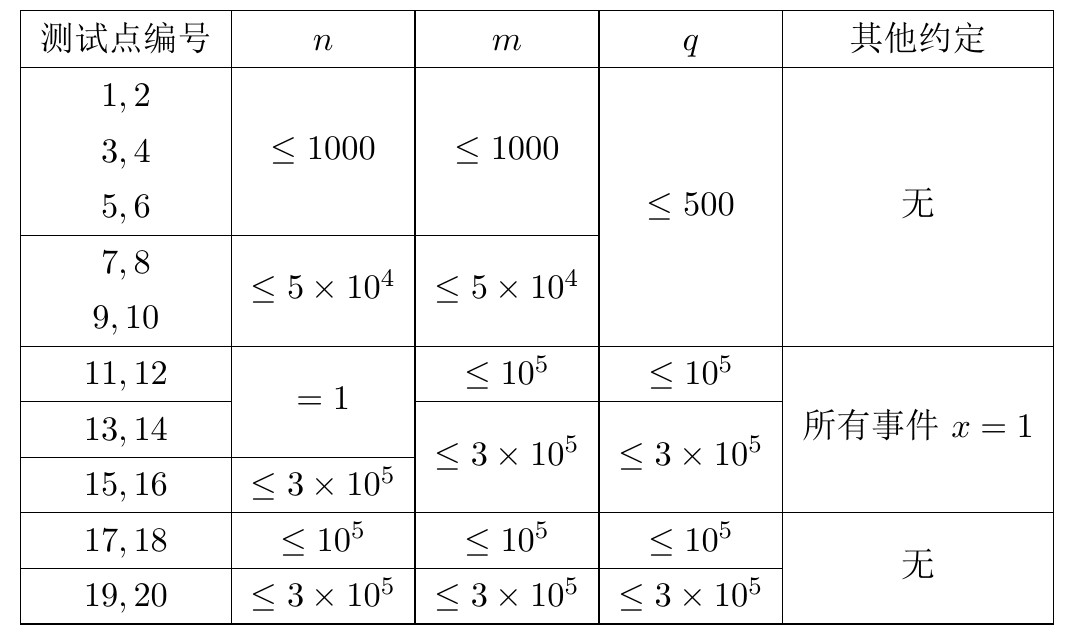
思路
果然有数据结构题,然而并不会做。不过部分分很丰富,有点天天爱跑步的感觉。
前30%直接暴力,而50%比较有趣,$q\le500$,远小于矩阵规模,可见很多行除第$m$列外根本不会变。那么可以在每次询问时如果$x$行第一次出现,暴力构建,再进行操作,当然也要维护第$m$列的数。每行的数据可以用一个指针数组或者std::vector记录。
再考虑$n=1$的情况,问题简化为一个数列,每次删除一个数,把它放在最后。随机访问的链表?好像不太对。不过如果不删除数,只是简单的打标记$flag_y$,然后最后新增,问题就转换为求第一个$i\vert i-\sum_{j=1}^i flag_j=y$,显然可以二分。前缀和可以用树状数组维护,$\log^2 n$,如果线段树树上二分可以做到$\log n$,完美解决。具体实现时,发现不必写递归版的线段树,非递归的更简单。
如果只有$x=1$,发现只要用队列维护第$m$列即可。
好像输入输出很大,想到模拟赛fstream被卡常的经历,我还写了输入输出优化。
时间复杂度,预计得分80
代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
#include <cstdio>
#include <cctype>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
const int N = 50005, N2 = 600005, SZ = 1e6;
unsigned last[N], *a[N];
int tree[N2 * 4];
long long val[N2];
FILE *fin = fopen("phalanx.in", "r"), *fout = fopen("phalanx.out", "w");
char ibuf[SZ], *ip = ibuf, *iend = ibuf, obuf[SZ], *op = obuf, *oend = obuf + SZ;
inline char nextchar()
{
if (ip == iend)
{
iend = ibuf + fread(ibuf, 1, SZ, fin);
ip = ibuf;
}
return *ip++;
}
inline void nextchar(char c)
{
if (op == oend)
{
fwrite(obuf, 1, SZ, fout);
op = obuf;
}
*op++ = c;
}
template <typename Int>
inline void read(Int &x)
{
char c;
for (c = nextchar(); isspace(c); c = nextchar())
;
x = 0;
for (; isdigit(c); c = nextchar())
x = x * 10 + c - '0';
}
int dig[20];
template <typename Int>
inline void writeln(Int x)
{
int len = 0;
do
dig[++len] = x % 10;
while (x /= 10);
for (; len; len--)
nextchar(dig[len] + '0');
nextchar('\n');
}
int main()
{
int n, m, q;
read(n);
read(m);
read(q);
if (n <= 5e4 && m <= 5e4 && q <= 500)
{
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
last[i] = 1u * i * m;
while (q--)
{
int x, y;
read(x);
read(y);
if (!a[x])
{
a[x] = new unsigned[m + 1];
for (int i = 1; i < m; i++)
a[x][i] = 1u * (x - 1) * m + i;
}
a[x][m] = last[x];
unsigned tmp = a[x][y];
for (int i = y + 1; i <= m; i++)
a[x][i - 1] = a[x][i];
for (int i = x + 1; i <= n; i++)
last[i - 1] = last[i];
last[n] = tmp;
writeln(tmp);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
if (a[i])
delete[] a[i];
}
else
{
//solve x=1
queue<long long> last;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
last.push(1ll * i * m);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
val[i] = i;
for (int t = 1; t <= q; t++)
{
int x, y;
read(x);
read(y);
int id = 1, l = 1, r = m + q, sum = 0;
while (l < r)
{
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
if (mid - tree[id * 2] - sum >= y)
{
r = mid;
id *= 2;
}
else
{
sum += tree[id * 2];
l = mid + 1;
id = id * 2 + 1;
}
}
long long tmp = val[l];
tree[id] = 1;
while (id > 1)
tree[id /= 2]++;
last.pop();
last.push(tmp);
val[m + t] = last.front();
writeln(tmp);
}
}
fwrite(obuf, 1, op - obuf, fout);
return 0;
}
剩下的时间
我感觉day2比day1简单,听说不少人T1出现了一些偏差。而T3我也很高兴拿了这么多部分分。快到时,选手程序已经公开,cfb在洛谷上交他的程序,车上气氛活跃。大约16点回到学校西门。
我们去机房交自己的程序,看洛谷的数据。我手忙脚乱的改输入输出,还CE了一次。所幸我的成绩没有太大的偏差,反而高了。洛谷比赛结束时有3.4K用户参加排名,其中有45个AK。

几天后
洛谷455,绍一490,学军420,波动比较大。不过据说洛谷的分数比较准确。
初测440,浙江省Rank125,学校Rank18,年段第六。浙江一等奖分数线据说大约395。
| math | complex | park | cheese | treasure | phalanx | 总分 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 60 | 100 | 30 | 100 | 70 | 80 | 440 |
浙江省分数线360,共305人获奖,大约53%……因为特派员已经被提高了5分……
按照公式有理有据,自从历年一等奖不占名额后,一等奖人数大幅增加。明年350人应该没问题了。